There are a variety of specific surface area analysis and testing methods. Among them, the gas adsorption method is widely used in various industries at home and abroad because of its scientific testing principle, the reliability of the test process, and the consistency of the test results, and gradually replaces other ratios. The surface area test method has become the most recognized test method. Many international standards organizations have listed the gas adsorption method as the specific surface area test standard, such as ASTM D3037 of the United States and ISO-9277 of the international ISO standards organization. There are many industry standards for specific surface area testing in China, the most representative of which is the national standard GB / T 19587-2004 "Determination of Specific Surface Area of ​​Solid Matters by Gas Adsorption BET Method".
The principle of measuring specific surface area by gas adsorption method is based on the adsorption characteristics of gas on a solid surface. Under a certain pressure, the surface of the sample particle (adsorbent) under test has a reversible physical adsorption effect on gas molecules (adsorbate) at ultra-low temperature There is a certain equilibrium adsorption amount corresponding to a certain pressure. By measuring this equilibrium adsorption amount, the specific surface area of ​​the sample to be measured is equivalently determined using a theoretical model. Due to the irregularity of the outer surface of the actual particle, strictly speaking, this method measures the total surface area of ​​the outer surface of the particle and the internal through holes that can be reached by the adsorbate molecules, as shown in the figure.
Nitrogen has become the most commonly used adsorbate due to its easy availability and good reversible adsorption characteristics. The specific surface area measured by this method is called the "equivalent" specific surface area. The concept of "equivalent" refers to: the specific surface area of ​​the sample is the number and molecules of nitrogen molecules coated (adsorbed) by the close packing of its surface Characterized by the maximum cross-sectional area. The equilibrium saturation adsorption capacity (V) of nitrogen molecules on the sample surface is actually measured, and the single layer saturation adsorption capacity (Vm) is calculated by different theoretical models, and then the number of molecules is obtained, and the nitrogen molecule equivalence is calculated using the surface close-packed hexagonal model The maximum cross-sectional area (Am), you can find the specific surface area of ​​the measured sample. Calculated as follows:
sg: measured sample specific surface area (m2 / g)
Vm: Saturated adsorption capacity of nitrogen molecules in a single layer (ml)
Am: equivalent maximum cross-sectional area of ​​nitrogen molecules (close-packed hexagonal theoretical value Am = 0.162 nm2)
W: Quality of the tested sample (g)
N: Avogadro's constant (6.02x1023)
Substituting the above data, the basic formula for calculating specific surface area by nitrogen adsorption method is obtained:
It can be seen from the above formula that the accurate determination of the single-layer saturated adsorption amount Vm on the sample surface is the key to the measurement of specific surface area.
Test method classification
There are two classification standards for the specific surface area test method. One is that it can be divided into: continuous flow method, volume method and weight method according to the method of determining the amount of gas adsorbed by the sample. The weight method is basically rarely used now; furthermore, it can be divided according to the different theoretical methods of calculating specific surface area: Specific surface area analysis and determination by direct contrast method, Langmuir method specific surface area analysis and measurement, BET method specific surface area analysis and measurement, etc. At the same time, the two classification standards have a certain relationship. The direct comparison method can only use the continuous flow method to determine the amount of adsorbed gas, and the BET method can use either the continuous flow method or the volume method to determine the amount of adsorbed gas. The relationship is shown in the figure.
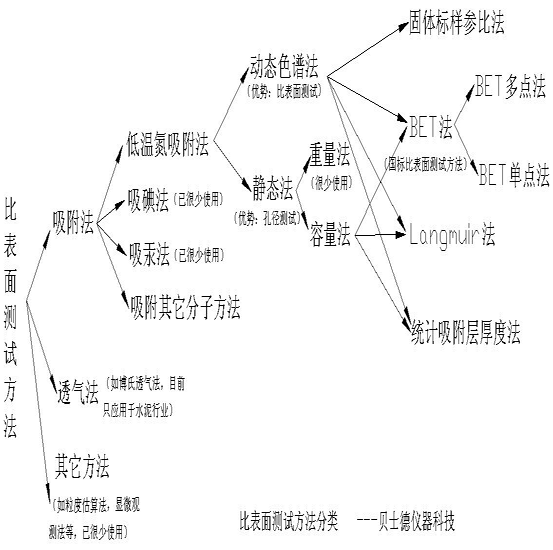
Continuous flow method
The continuous flow method is relative to the static method. The entire test process is carried out under normal pressure. The adsorbent is adsorbed in a continuous flow state. The continuous flow method is developed on the basis of the principle of gas chromatography. The thermal conductivity detector is used to determine the amount of gas adsorbed by the sample. Continuous dynamic nitrogen adsorption uses nitrogen as the adsorption gas and helium or hydrogen as the carrier gas. The two gases are mixed in a certain ratio to make the nitrogen reach the specified relative pressure and flow through the surface of the sample particles. When the sample tube is placed in a liquid nitrogen environment, the powder material physically adsorbs the nitrogen in the mixed gas, but the carrier gas will not be adsorbed, causing the composition ratio of the mixed gas to change, resulting in a change in thermal conductivity. When the signal voltage is detected from the thermal conductivity detector, an adsorption peak appears. After the adsorption is saturated, let the sample return to room temperature, and the adsorbed nitrogen will be desorbed, forming a desorption peak opposite to the adsorption peak. The area of ​​the adsorption peak or desorption peak is proportional to the amount of nitrogen adsorbed on the sample surface. The amount of nitrogen represented by the peak area can be calibrated by quantitative gas. By measuring the amount of nitrogen adsorbed on a series of nitrogen partial pressures P / P0, the nitrogen isothermal adsorption or desorption curve can be drawn, and then the specific surface area can be obtained. The desorption peak is usually used to calculate the specific surface area.
Features: The continuous flow method has a simple operation process and a strong ability to eliminate system errors. At the same time, it can use the direct comparison method and BET method to calculate the specific surface area.
Volumetric method In the volumetric method, the amount of gas adsorbed by the sample is measured using the gas equation. Introduce a certain amount of adsorbed gas into the pre-evacuated closed system. By measuring the change of gas pressure in the closed system caused by the adsorption and desorption of the sample, use the gas state equation P * V / T = nR to calculate the change in the number of moles of adsorbed gas.
Direct comparison
The direct comparison method specific surface area analysis test uses the continuous flow method to determine the amount of adsorbed gas. In the measurement process, a standard sample (a stable substance whose specific surface area is strictly calibrated) needs to be selected. Connected in parallel to the test gas path exactly the same as the tested sample, through the simultaneous adsorption with the tested sample, desorption, respectively, to determine the respective desorption peak. Under the same adsorption and desorption conditions, the specific surface area of ​​the tested sample and the standard sample is proportional to its peak area. Calculated as follows:
Sx: specific surface area of ​​the tested sample S0: specific surface area of ​​the standard sample,
Ax: Desorbed peak area of ​​tested sample A0: Desorbed peak area of ​​standard sample
Wx: quality of the tested sample W0: quality of the standard sample
Advantages: The specific surface area can be obtained without actually calibrating the adsorbed nitrogen volume and complicated theoretical calculations; the test operation is simple, the test speed is fast, and the efficiency is high. Disadvantages: When the surface adsorption characteristics of the standard sample and the measured sample are very different, If the number of adsorption layers is different, the test result error will be larger.
The direct comparison method is only suitable for the measurement of samples that are close to the adsorption characteristics of the standard sample. Because the BET method has a more reliable theoretical basis, the measurement of the specific surface area by the BET method is more generally accepted at home and abroad.
BET specific surface area test method
The BET theoretical calculation is based on the multi-molecular layer adsorption formula derived from the classic statistical theory by Brunauer, Emmett and Teller, namely the famous BET equation:
P: Partial pressure of adsorbate P0: Saturated vapor pressure of adsorbent
V: actual sample adsorption capacity Vm: single layer saturation adsorption capacity
C: The constants related to the adsorption capacity of the sample can be seen from the above formula. The BET equation establishes the quantitative relationship between the single-layer saturated adsorption capacity Vm and the multi-layer adsorption capacity V, which provides a good theoretical basis for the measurement of specific surface area.
The BET equation is based on the theory of multi-layer adsorption, which is closer to the actual adsorption process of many substances, so the test results are more reliable. In the actual test process, usually measure 3-5 groups of tested samples under different gas partial pressures, multi-layer adsorption capacity V, with P / P0 as the X axis, For the Y axis, a linear fit is made from the BET equation, and the slope and intercept of the straight line are obtained, so that the Vm value is calculated to calculate the specific surface area of ​​the sample to be measured. Theory and practice show that when the P / P0 point is in the range of 0.05-0.35, the BET equation is consistent with the actual adsorption process, and the graph linearity is also very good, so the point selection in the actual test process needs to be within this range. Since 3-5 groups of P / P0 are selected for measurement, we usually call it multi-point BET. When the adsorption capacity of the tested sample is very strong, that is, the C value is large, the intercept of the straight line is close to zero, and it can be approximated that the straight line passes through the origin. At this time, only a set of P / P0 data can be measured and connected to the origin to find the specific surface area , We call it single point BET. Compared with multi-point BET, the error of single-point BET results will be larger.
If the flow method is used for BET determination, the measurement system needs to be equipped with a device that can accurately adjust the gas partial pressure P / P0 to achieve the determination of the adsorption amount under different P / P0. For each point P / P0, the process of BET adsorption and desorption is similar to the direct comparison method. The difference is that the BET method needs to calibrate the volume of the actual gas adsorbed by the sample, but the direct comparison method does not.
Features: The BET theory is closer to the actual adsorption process of the substance, with a wide range of measurable samples, high accuracy and credibility of the test results, and is particularly suitable for scientific research and production units.
Pore ​​size distribution test
The gas adsorption method pore size (porosity) distribution measurement uses the principle of capillary condensation and volume equivalent substitution, that is, the amount of liquid nitrogen filled in the measured pore is equivalent to the pore volume. The adsorption theory assumes that the shape of the hole is a cylindrical tube, thus establishing a capillary condensation model. According to the capillary aggregation theory, under different P / P0, the range of pore diameters that can cause capillary aggregation is different. As the value of P / P0 increases, the radius of pores that can cause aggregation also increases. Corresponding to a certain value of P / P0, there is a critical pore radius Rk. All pores with a radius less than Rk are capillary condensed, liquid nitrogen is filled in them, and pores larger than Rk will not be capillary condensed, and liquid nitrogen will not be in them. filling. The critical radius can be given by the Kelvin equation:
Rk is called the Kelvin radius, and it depends entirely on the relative pressure P / P0. The Kelvin formula can also be understood as that for pores that have undergone condensation, when the pressure is below a certain P / P0, the condensate in pores with a radius greater than Rk will vaporize and desorb. Theory and practice show that capillary condensation occurs only when P / P0 is greater than 0.4. By measuring the amount of nitrogen condensed at different P / P0, the isothermal adsorption and desorption curve can be drawn. Through different theoretical methods The curve of pore volume and pore size distribution is obtained. The most commonly used calculation method is the use of BJH theory, commonly referred to as BJH pore volume and pore size distribution.
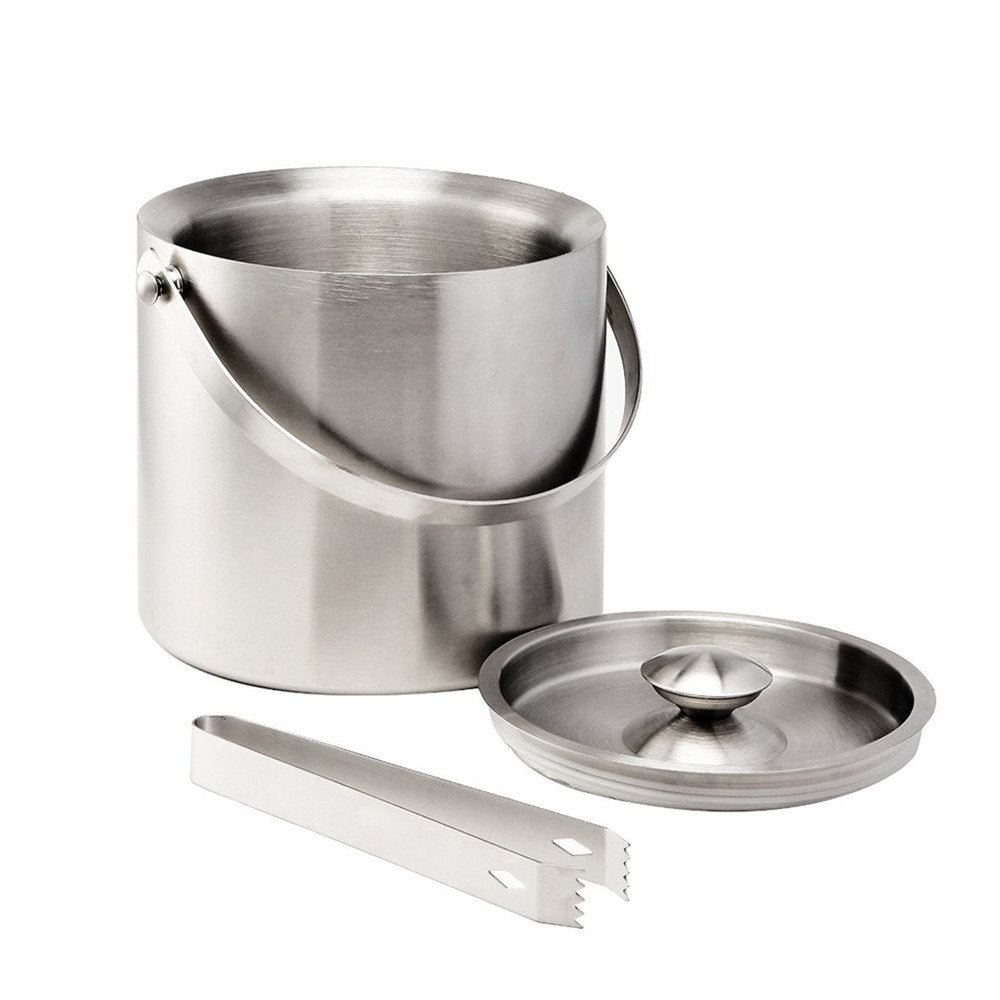
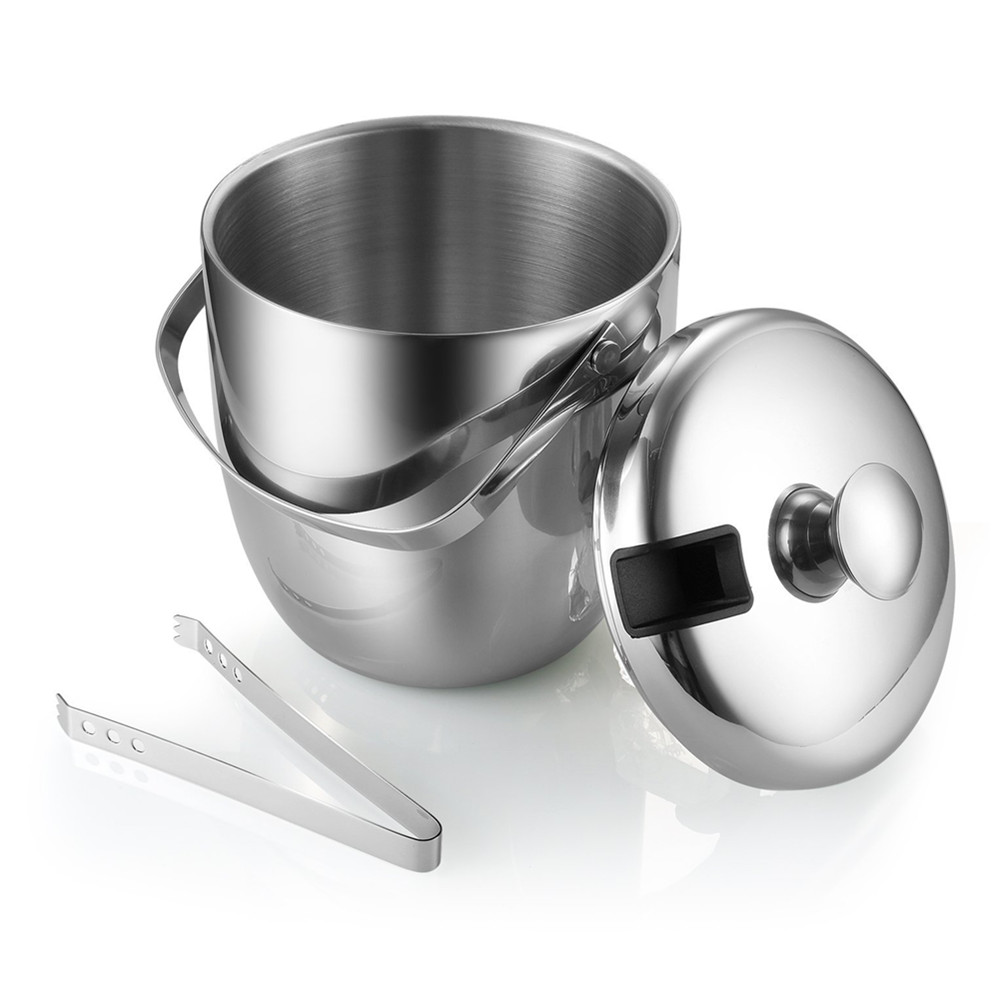
Ice Bucket
1:Brushed stainless steel body resists fingerprints,Double-wall Ice Bucket keeps cold inside and prevents outer condensation
2:Food safe and dishwasher safe
3: Equipped with lid and handles for convenient carrying. Includes stainless steel scoop that works better than prongs.
4:Suitable for party, weddings, picnics and so on.
Any ideas or OEM requirement about our ice bucket items,please feel free to talk with us.
Description of Ice Bucket
Material:SS304
Finishing: Satin polishing ,Mirror Polishing ,Color painting
Logo: Laser logo, Etching logo, Silk printing logo, Embossed logo, Decal logo
MOQ : 2000 PCS
Packaging : White box, Mail box or Customized package
Sample Time : 7~10 days
Lead Time :60 days after have the deposit
Payment: T/T ,L/C or others
Payment term: 30% deposit before production and 70 % balance against the copy B/L



Welcome to contact us for more details and Professional product recommendation .
Waiting for your inquiry.
Ice Bucket
Stainless Steel Ice Bucket,Double Wall Ice Bucket,Ice Buckets With Lids,Stainless Steel Wine Bucket
Jiangmen Wellway Houseware Co.,Ltd , https://www.wellwayhouseware.com