2.3 Toughener Selection
Toughening modification methods for epoxy resins can be roughly divided into: (1) adding modifiers to form two-phase structures; (2) changing the chemical structure of cross-linked networks; (3) forming semi-IPNs with thermoplastic resins Wear network); (4)
Controls the heterogeneity of molecular cross-linking states. As a structural adhesive commonly used nitrile rubber toughened epoxy resin. In particular, nitrile rubbers with reactive end groups (such as fluorene groups, amino groups, etc.) react with epoxy resins to form blocks. In the curing process of epoxy resins, these rubbers are generally folded out of the epoxy resin and physically. The formation of two-phase structure morphology, significantly improve the fracture toughness of epoxy resin. But at the same time other properties of the system, such as heat distortion temperature and certain mechanical properties, may decrease. In addition, in the process of rubber toughening epoxy, although most of the rubber is precipitated from the epoxy matrix to form a two-phase structure, there is still a small part of the rubber “dissolved†in the epoxy matrix to play a “softening†effect. As a result, the modulus and the glass transition temperature of the modified epoxy resin decrease. This is the inadequacy of rubber toughened epoxy resins. To overcome its deficiencies, use tough heat resistant plastic resin, such as phenolic oxygen, polysulfone resin modified epoxy. Due to its high Tg and modulus, the modified epoxy resin does not reduce its Tg and modulus, but also improves toughness. As polysulfone is added to the epoxy resin, a semi-IPN (interpenetrating network) structure can be formed. The thermoplastic resin continuously penetrates the network of the thermosetting epoxy resin to increase its toughness.
The amount of polysulfone resin should be appropriate. No polysulfone resin, can not be made into flakes; too much to add, difficult to crush.
2.4 Synthesis and Screening Softening Point Regulators
The softening point of the B-state resin is adjusted so that it is convenient for low-temperature crushing and is not susceptible to thermal adhesion, but also creates favorable conditions for foaming (once it reaches a certain temperature, it can fully flow and reduce the viscosity of the entire system).
2.5 Selection of foaming agent
Because it needs to be cured at 120-130°C, the softening point of the resin is between 80 and 90°C. We chose azobisisobutyronitrile as the blowing agent through experiments.
2.6 The influencing factors and basic properties of the glue are as follows:
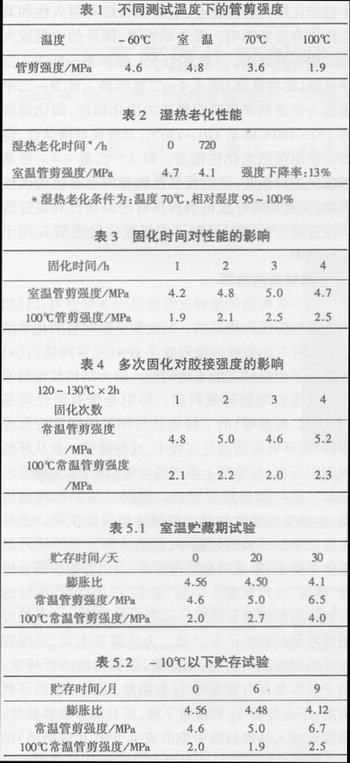
(to be continued)
Braided Line,PE Braided Line,Braided Fishing Line
Organized & storage plastic boxes Fishing swivels co.,ltd , http://www.nsfishingtackle.com